Spaceship Game Using Python With Source Code
Introduction :
In this blog post, we’ll dive into creating a classic spaceship game using Python. This game, reminiscent of the iconic Asteroids, involves controlling a spaceship, shooting missiles, and navigating through space while avoiding asteroids. We’ll use the SimpleGUI library to handle graphics and animations In this project, we’ll build a space-themed game where players control a spaceship, shoot missiles, and avoid asteroids. The game involves moving the spaceship, shooting at asteroids, and navigating through a dynamic environment with animations and sound effects. This game is designed to be both entertaining and a great way to practice Python programming.
Required Modules or Packages:-
To run this project, you will need to install the SimpleGUI library, which provides an easy way to create graphical user interfaces and handle animations. You can install it using pip
pip install simplegui
The project also uses external image and sound files. Ensure you have internet access to load
these assets.
How to Run the Code :-
1. Clone the Repository:
○ Cloneor download the code from the provided repository.
2. Install Dependencies:
○ Ensure you have SimpleGUI installed.
3. Runthe Code:
Execute the script using Python:
python spaceship_game.py
4. Play the Game:
○ Usethearrow keys to navigate the spaceship and the space bar to shoot missiles.
Code Explanation :-
Let’s break down the key components of the code:
1. Global Variables and Constants
● WIDTHandHEIGHT:Define the dimensions of the game window.
● scoreandlives: Track the player’s score and remaining lives.
● time: Used for animating the background.
2. ImageInfo Class
Handles image attributes like center, size, radius, and lifespan. It’s used to manage the various
game assets such as the spaceship, missiles, and asteroids.
3. Ship Class
● Attributes: Position, velocity, angle, and image of the spaceship.
● Methods:
○ draw(): Draws the spaceship on the canvas.
○ update(): Updates the spaceship’s position and velocity based on user input.
○ thrust_up(): Activates thrust and changes the spaceship’s image.
○ stop_thrust(): Stops the thrust and resets the image.
○ shoot(): Fires a missile from the spaceship.
4. Sprite Class
Handles all other sprites in the game, such as asteroids and missiles:
● Attributes: Position, velocity, angle, and image of the sprite.
● Methods:
○ draw(): Draws the sprite on the canvas.
○ update(): Updates the sprite’s position and angle.
5. Helper Functions
● angle_to_vector(): Converts an angle to a unit vector.
● dist(): Calculates the distance between two points.
6. Draw Handler
● animates the background with moving debris and nebula images.
● drawsthe spaceship and sprites on the canvas.
● updates the game state, including the spaceship, asteroids, and missiles.
7. Rock Spawner
Spawns new asteroids at random positions and velocities.
8. Key Handlers
● keydown_handler(): Handles key presses for spaceship movement and shooting.
● keyup_handler(): Stops thrusting when the up arrow key is released.
9. Game Initialization
● Creates a gamewindow and initializes the spaceship and other sprites.
● Registers event handlers for drawing, key presses, and the rock spawner
Get Discount on Top Educational Courses
Source Code :
# Program template for Spaceship
import simplegui
import math
import random
# Globals for user interface
WIDTH = 800
HEIGHT = 600
score = 0
lives = 3
time = 0.5
# Global constants
CST_ANG_VEL = 0.07 # Constant angle velocity of ship
CST_ACC_SPEED = 0.055 # Constant acceleration speed of ship
COE_FRI = 0.008 # Coefficient of friction
MIS_SPEED = 10 # Constant missile speed
# ImageInfo class and asset loading
class ImageInfo:
def __init__(self, center, size, radius=0, lifespan=None, animated=False):
self.center = center
self.size = size
self.radius = radius
self.lifespan = lifespan if lifespan else float('inf')
self.animated = animated
def get_center(self):
return self.center
def get_size(self):
return self.size
def get_radius(self):
return self.radius
def get_lifespan(self):
return self.lifespan
def get_animated(self):
return self.animated
# Helper functions
def angle_to_vector(ang):
return [math.cos(ang), math.sin(ang)]
def dist(p, q):
return math.sqrt((p[0] - q[0]) ** 2 + (p[1] - q[1]) ** 2)
# Ship class
class Ship:
def __init__(self, pos, vel, angle, image, info):
self.pos = [pos[0], pos[1]]
self.vel = [vel[0], vel[1]]
self.thrust = False
self.angle = angle
self.angle_vel = 0
self.image = image
self.image_center = info.get_center()
self.image_size = info.get_size()
self.radius = info.get_radius()
def draw(self, canvas):
canvas.draw_image(self.image, self.image_center, self.image_size, self.pos, self.image_size, self.angle)
def update(self):
self.angle += self.angle_vel
vec = [0, 0]
ang_t_vel = angle_to_vector(self.angle)
if self.thrust:
vec = [ang_t_vel[0] * CST_ACC_SPEED, ang_t_vel[1] * CST_ACC_SPEED]
friction = [self.vel[0] * COE_FRI, self.vel[1] * COE_FRI]
self.vel[0] += (vec[0] - friction[0])
self.vel[1] += (vec[1] - friction[1])
self.pos[0] += self.vel[0]
self.pos[1] += self.vel[1]
self.pos[0] %= WIDTH
self.pos[1] %= HEIGHT
def thrust_up(self):
self.thrust = True
self.image_center[0] = 135
ship_thrust_sound.play()
def stop_thrust(self):
self.thrust = False
self.image_center[0] = 45
ship_thrust_sound.rewind()
def shoot(self):
global a_missile
ang_t_vel = angle_to_vector(self.angle)
a_missile = Sprite(
[self.pos[0] + (self.radius + 7) * ang_t_vel[0], self.pos[1] + (self.radius + 7) * ang_t_vel[1]],
[self.vel[0] + ang_t_vel[0] * MIS_SPEED, self.vel[1] + ang_t_vel[1] * MIS_SPEED],
0, 0, missile_image, missile_info, missile_sound
)
# Sprite class
class Sprite:
def __init__(self, pos, vel, ang, ang_vel, image, info, sound=None):
self.pos = [pos[0], pos[1]]
self.vel = [vel[0], vel[1]]
self.angle = ang
self.angle_vel = ang_vel
self.image = image
self.image_center = info.get_center()
self.image_size = info.get_size()
self.radius = info.get_radius()
self.lifespan = info.get_lifespan()
self.animated = info.get_animated()
self.age = 0
if sound:
sound.rewind()
sound.play()
def draw(self, canvas):
canvas.draw_image(self.image, self.image_center, self.image_size, self.pos, self.image_size, self.angle)
def update(self):
self.angle += self.angle_vel
self.pos[0] += self.vel[0]
self.pos[1] += self.vel[1]
self.pos[0] %= WIDTH
self.pos[1] %= HEIGHT
def draw(canvas):
global time
time += 1
wtime = (time / 4) % WIDTH
center = debris_info.get_center()
size = debris_info.get_size()
canvas.draw_image(nebula_image, nebula_info.get_center(), nebula_info.get_size(), [WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT / 2], [WIDTH, HEIGHT])
canvas.draw_image(debris_image, center, size, (wtime - WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT / 2), (WIDTH, HEIGHT))
canvas.draw_image(debris_image, center, size, (wtime + WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT / 2), (WIDTH, HEIGHT))
my_ship.draw(canvas)
my_ship.update()
a_missile.draw(canvas)
a_missile.update()
for rock in rock_set:
rock.draw(canvas)
rock.update()
for explosion in explosion_set:
explosion.draw(canvas)
explosion.update()
def keydown(key):
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['left']:
my_ship.angle_vel = -CST_ANG_VEL
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['right']:
my_ship.angle_vel = CST_ANG_VEL
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
my_ship.thrust_up()
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['space']:
my_ship.shoot()
def keyup(key):
if key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['left']:
my_ship.angle_vel = 0
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['right']:
my_ship.angle_vel = 0
elif key == simplegui.KEY_MAP['up']:
my_ship.stop_thrust()
def rock_spawner():
global rock_set
if len(rock_set) < 12:
pos = [random.randrange(0, WIDTH), random.randrange(0, HEIGHT)]
vel = [random.random() * 2 - 1, random.random() * 2 - 1]
ang_vel = random.random() * 0.2 - 0.1
a_rock = Sprite(pos, vel, 0, ang_vel, asteroid_image, asteroid_info)
rock_set.add(a_rock)
# Initialize the game
frame = simplegui.create_frame("Spaceship Game", WIDTH, HEIGHT)
frame.set_draw_handler(draw)
frame.set_keydown_handler(keydown)
frame.set_keyup_handler(keyup)
frame.set_timer_handler(1000, rock_spawner)
# Initialize ship
my_ship = Ship([WIDTH / 2, HEIGHT / 2], [0, 0], 0, ship_image, ship_info)
# Initialize missile
a_missile = Sprite([0, 0], [0, 0], 0, 0, missile_image, missile_info)
# Initialize rock set
rock_set = set()
# Start the frame
frame.start()
Output :
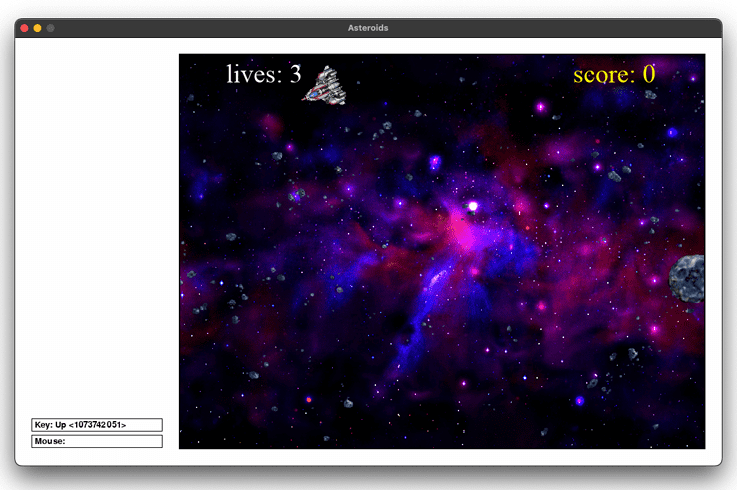
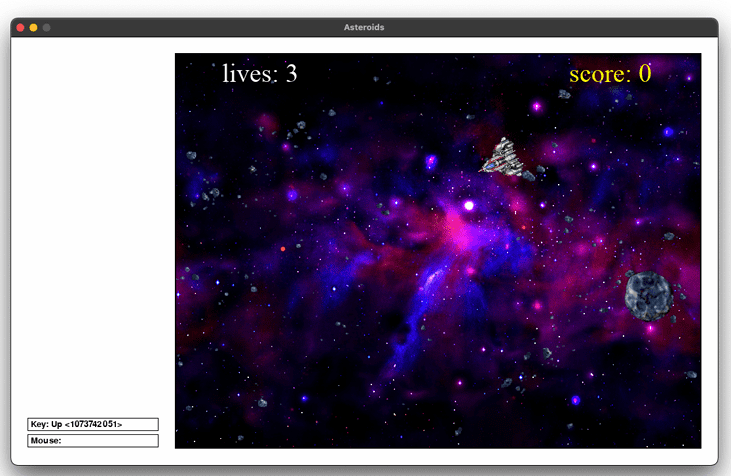
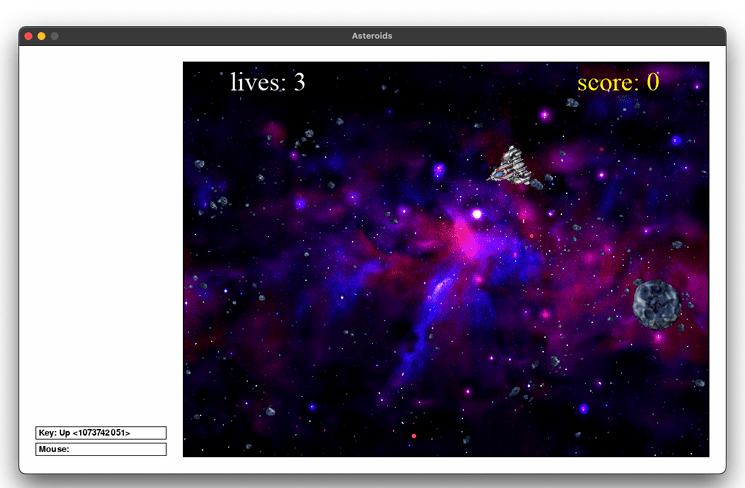
Find More Projects
resume screener in python using python introduction The hiring process often begins with reviewing numerous resumes to filter out the most suitable …
expense tracer in python using GUI introduction Tracking daily expenses is a vital part of personal financial management. Whether you’re a student …
my personal diary in python using GUI introduction Keeping a personal diary in python is one of the oldest and most effective …
interview question app in python using GUI introduction In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, landing a job often requires more than just …
sudoko solver in python using GUI introduction Sudoku, a classic combinatorial number-placement puzzle, offers an engaging challenge that blends logic, pattern recognition, …
handwritten digit recognizer in python introduction In an era where artificial intelligence and deep learning are transforming industries, real-time visual recognition has …