Temperature Converter in Java using Swing With Source Code
Introduction:
The Temperature Converter is a common tool used in daily life and has various applications in different fields such as meteorology, thermodynamics, and physics. With the rise of computer technology, it is now possible to build a graphical user interface (GUI) for this tool,making it easier and more convenient to use. Java, with its rich libraries and versatility, is an ideal choice for building such an application.In this article, we will be building a Temperature Converter in Java using the Swing library. Swing is a rich set of graphical user interface components that can be used to create a variety of graphical applications.We will use Swing to create the user interface of our Temperature Converter and the Java programming language to perform the temperature conversions.
Explanation:
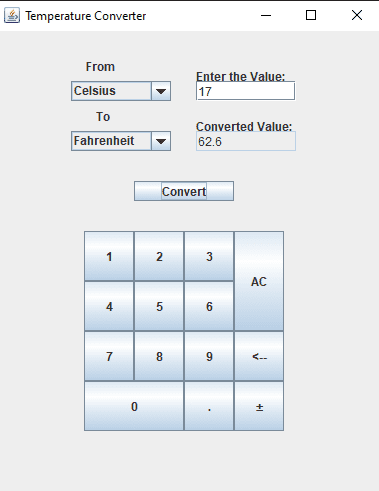
The Temperature Converter in Java using Swing is a GUI application that allows users to convert temperatures from Celsius to Fahrenheit and vice versa. The application is built using the Java programming language and the Swing library , which provides a rich set of graphical user interface components. The user interface consists of two text fields, one for entering the temperature value in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, and another for displaying the converted temperature. There are also two buttons,one for converting from Celsius to Fahrenheit and another for converting from Fahrenheit to Celsius.
The application works by using the event-driven programming paradigm. The user enters a temperature value in either Celsius or Fahrenheit, and when the conversion button is clicked, the application performs the necessary calculation and displays the result in the other unit. The temperature conversion formula is as follows:
Celsius to Fahrenheit: (°C x 9/5) + 32 = °F Fahrenheit to Celsius: (°F – 32) x 5/9 = °C
The application follows the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern, which separates the data and business logic of the application from its user interface. This helps to make the application more modular, maintainable, and easier to update.
Source Code:
Get Discount on Top Educational Courses
/**
*
* @author CODE_WITH_CURIOUS
*/
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class TC extends JFrame {
JLabel l1, l2, l3, l4;
JComboBox tc1, tc2;
JTextField t1, t2;
JButton b, dot, ac, bs, pm;
JButton n0, n1, n2, n3, n4, n5, n6, n7, n8, n9;
public TC(String s) {
super(s);
}
public void setComp() {
String arr1[] = { "Celsius", "Fahrenheit", "Kelvin", "Rankine", "Reaumur" };
String arr2[] = { "Celsius", "Fahrenheit", "Kelvin", "Rankine", "Reaumur" };
l1 = new JLabel("To");
l2 = new JLabel("Enter the Value:");
l3 = new JLabel("Converted Value:");
l4 = new JLabel("From");
tc1 = new JComboBox(arr1);
tc2 = new JComboBox(arr2);
t1 = new JTextField();
t2 = new JTextField();
b = new JButton("Convert");
dot = new JButton(".");
pm = new JButton("±");
bs = new JButton("<--");
ac = new JButton("AC");
n0 = new JButton("0");
n1 = new JButton("1");
n2 = new JButton("2");
n3 = new JButton("3");
n4 = new JButton("4");
n5 = new JButton("5");
n6 = new JButton("6");
n7 = new JButton("7");
n8 = new JButton("8");
n9 = new JButton("9");
setLayout(null);
tc1.setBounds(75, 50, 100, 20);
t1.setBounds(200, 50, 100, 20);
l1.setBounds(100, 75, 50, 20);
l4.setBounds(90, 25, 50, 20);
l2.setBounds(200, 35, 100, 20);
l3.setBounds(200, 85, 100, 20);
tc2.setBounds(75, 100, 100, 20);
t2.setBounds(200, 100, 100, 20);
b.setBounds(138, 150, 100, 20);
ac.setBounds(238, 200, 50, 100);
pm.setBounds(238, 350, 50, 50);
bs.setBounds(238, 300, 50, 50);
dot.setBounds(188, 350, 50, 50);
n0.setBounds(88, 350, 100, 50);
n1.setBounds(88, 200, 50, 50);
n2.setBounds(138, 200, 50, 50);
n3.setBounds(188, 200, 50, 50);
n4.setBounds(88, 250, 50, 50);
n5.setBounds(138, 250, 50, 50);
n6.setBounds(188, 250, 50, 50);
n7.setBounds(88, 300, 50, 50);
n8.setBounds(138, 300, 50, 50);
n9.setBounds(188, 300, 50, 50);
b.addActionListener(new Handler());
ac.addActionListener(new Handler());
pm.addActionListener(new Handler());
bs.addActionListener(new Handler());
dot.addActionListener(new Handler());
n0.addActionListener(new Handler());
n1.addActionListener(new Handler());
n2.addActionListener(new Handler());
n3.addActionListener(new Handler());
n4.addActionListener(new Handler());
n5.addActionListener(new Handler());
n6.addActionListener(new Handler());
n7.addActionListener(new Handler());
n8.addActionListener(new Handler());
n9.addActionListener(new Handler());
add(tc1);
add(tc2);
add(l1);
add(l2);
add(l3);
add(l4);
add(t1);
add(t2);
add(b);
add(ac);
add(dot);
add(pm);
add(bs);
add(n0);
add(n1);
add(n2);
add(n3);
add(n4);
add(n5);
add(n6);
add(n7);
add(n8);
add(n9);
t2.setEditable(false);
}
class Handler implements ActionListener {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String x, y;
x = (String) tc1.getSelectedItem();
y = (String) tc2.getSelectedItem();
if (e.getSource() == n0)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "0");
if (e.getSource() == n1)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "1");
if (e.getSource() == n2)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "2");
if (e.getSource() == n3)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "3");
if (e.getSource() == n4)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "4");
if (e.getSource() == n5)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "5");
if (e.getSource() == n6)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "6");
if (e.getSource() == n7)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "7");
if (e.getSource() == n8)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "8");
if (e.getSource() == n9)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + "9");
if (e.getSource() == dot)
t1.setText(t1.getText() + ".");
if (e.getSource() == ac) {
t1.setText("");
t2.setText("");
}
if (e.getSource() == pm) {
String spm = new String();
spm = t1.getText();
if (spm.length() == 0)
t1.setText("-");
else if (spm.charAt(0) != '-')
t1.setText("-" + t1.getText());
else
t1.setText("" + spm.substring(1));
}
if (e.getSource() == bs) {
int n;
String bsp = new String();
bsp = t1.getText();
n = bsp.length();
t1.setText("" + bsp.substring(0, n - 1));
}
if (e.getSource() == b) {
// Both are same.......................
if (x == "Celsius" && y == "Celsius") {
t2.setText("" + t1.getText());
} else if (x == "Fahrenheit" && y == "Fahrenheit") {
t2.setText("" + t1.getText());
} else if (x == "Kelvin" && y == "Kelvin") {
t2.setText("" + t1.getText());
} else if (x == "Rankine" && y == "Rankine") {
t2.setText("" + t1.getText());
} else if (x == "Reaumur" && y == "Reaumur") {
t2.setText("" + t1.getText());
}
// Celsius to others.........................
else if (x == "Celsius" && y == "Fahrenheit") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a * 9 / 5) + 32);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Celsius" && y == "Kelvin") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a + 273.15);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Celsius" && y == "Rankine") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 9 / 5 + 32 + 459.67);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Celsius" && y == "Reaumur") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 0.8);
t2.setText("" + b);
}
// Fahrenheit to others......................
else if (x == "Fahrenheit" && y == "Celsius") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 32) * 5 / 9);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Fahrenheit" && y == "Kelvin") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 32) * 5 / 9 + 273.15);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Fahrenheit" && y == "Rankine") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a + 459.67);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Fahrenheit" && y == "Reaumur") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 32) / 2.25);
t2.setText("" + b);
}
// Kelvin to others.........................
else if (x == "Kelvin" && y == "Celsius") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a - 273.15);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Kelvin" && y == "Fahrenheit") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 273.15) * 9 / 5 + 32);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Kelvin" && y == "Rankine") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 9 / 5);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Kelvin" && y == "Reaumur") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 273.15) * 0.8);
t2.setText("" + b);
}
// Rankine to others............................
else if (x == "Rankine" && y == "Celsius") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 32 - 459.67) / 1.8);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Rankine" && y == "Fahrenheit") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a - 459.67);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Rankine" && y == "Kelvin") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a / 1.8);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Rankine" && y == "Reaumur") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) ((a - 32 - 459.67) / 2.25);
t2.setText("" + b);
}
// Reaumur to others........................
else if (x == "Reaumur" && y == "Celsius") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 1.25);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Reaumur" && y == "Fahrenheit") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 2.25 + 32);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Reaumur" && y == "Kelvin") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 1.25 + 273.15);
t2.setText("" + b);
} else if (x == "Reaumur" && y == "Rankine") {
String s = t1.getText();
float a = Float.parseFloat(s);
float b = (float) (a * 2.25 + 32 + 459.67);
t2.setText("" + b);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TC jf = new TC("Temperature Converter");
jf.setComp();
jf.setSize(400, 500);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
In conclusion, the Temperature Converter in Java using Swing is a simple and easy-to-use application that can be used to quickly convert temperatures between Celsius and Fahrenheit. Its use of the Swing library and the MVC design pattern make it a great example of how to build a Java GUI application.
Output:
Find More Projects
URL Shortener Using Python Django Introduction: Long URLs can be shortened into short, shareable links with the help of the URL Shortener …
User Authentication System Using Python Django Introduction: The implementation of safe and adaptable user authentication in Django is the main goal of …
The E-Learning System using Java with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) Introduction The E-Learning System is developed using Java (with a Graphical …
Weather App Using Python Django Introduction: When a user enters the name of a city, the Weather App retrieves current weather information. …
Quiz App Using Python Django Introduction: Users can take quizzes in a variety of subjects, see their results, and monitor their progress …
resume screener in python using python introduction The hiring process often begins with reviewing numerous resumes to filter out the most suitable …