quiz application in python using jupyter
introduction
This project is a Multiple-Choice Quiz Application built using Python’s tkinter library, which provides a simple way to create desktop GUI applications. The primary goal of this app is to simulate an interactive quiz where users answer questions one by one and receive a final score based on their performance.
This project showcases the fundamentals of event-driven programming, where the flow of the program is determined by user interactions — such as button clicks or option selections. It is suitable for beginners who want hands-on experience with GUI development and building logic-based applications in Python.
Key Features of the Application:
Presents one question at a time with four answer options
Uses
Radiobuttonwidgets for single-choice answersValidates the user’s selection against the correct answer
Tracks and updates the user’s score in real time
Displays a summary of results at the end using a messagebox
Includes basic layout management, styling, and interactivity
Educational Objectives:
Understand how to create and manipulate widgets like
Label,Radiobutton,Button, andStringVarin TkinterLearn how to use global variables to maintain the application state (e.g., current question index, score)
Learn to store and access structured data using Python lists and dictionaries
Apply control flow logic (
if,else,for,global) in an event-based environment
Practical Applications:
This app can be the foundation for:
Educational assessments (quizzes for students)
Recruitment screening tools
Trivia games
Certification practice tests
Opportunities for Extension:
Add a countdown timer for each question
Load questions from an external JSON, CSV, or database file
Add a progress bar or score tracker display
Support for image-based or multimedia questions
Add feedback after each question (e.g., “Correct!” or “Wrong!”)
Create user login profiles and store scores for later review
steps to create quiz application
1. Import Required Modules
Import
tkinterandmessageboxfor GUI and popups.
2. Create the Quiz Question Bank
Define a list of dictionaries with:
"q": question text"a": list of options"c": correct answer
3. Initialize Game Variables
Set
current_q = 0to keep track of the current question.Initialize
score = 0to record correct answers.
4. Define a Function to Load Questions
Retrieve the current question using the index.
Set the question text to the
Label.Set each option text to the radio buttons.
5. Define a Function to Check the Selected Answer
Get selected option index using
var.get().Check if selected option matches the correct answer.
If correct, increase score.
Move to the next question or show final score using a popup.
6. Create the Main Tkinter Window
Initialize the window using
tk.Tk().Set title, dimensions, and background color.
7. Create the Question Label
Use a
StringVarandLabelto display the question.Enable wrapping so long questions fit nicely.
8. Create Option Buttons (Radio Buttons)
Use
IntVarfor tracking selected radio button.Loop to create 4
Radiobuttonoptions linked to the variable.
9. Add a “Next” Button
Use
Buttonto triggercheck_answer()function.After each click, the next question is loaded.
10. Start the Quiz Loop
Call
load_question()to display the first question.Call
root.mainloop()to keep the window running.
code explanation
1. Importing Required Modules
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
tkinteris used to create GUI elements.messageboxis used to show popup messages at the end of the quiz.
2. Defining Quiz Data
questions = [
{"q": "What is the capital of France?", "a": ["Paris", "London", "Rome", "Berlin"], "c": "Paris"},
{"q": "Which is a Python framework?", "a": ["Laravel", "React", "Django", "Angular"], "c": "Django"},
]
A list of dictionaries where each dictionary contains:
"q": the question text."a": a list of answer options."c": the correct answer.
3. Initialize Variables
current_q = 0
score = 0
current_qkeeps track of which question is currently displayed.scoretracks the number of correct answers.
4. Loading a Question into the GUI
def load_question():
q = questions[current_q]
question.set(q['q'])
for i in range(4):
options[i].config(text=q['a'][i])
Retrieves the current question and updates the label text and radio buttons with the question and answer options.
5. Checking the Selected Answer
def check_answer():
global current_q, score
selected = var.get()
if questions[current_q]['a'][selected] == questions[current_q]['c']:
score += 1
current_q += 1
if current_q < len(questions):
load_question()
else:
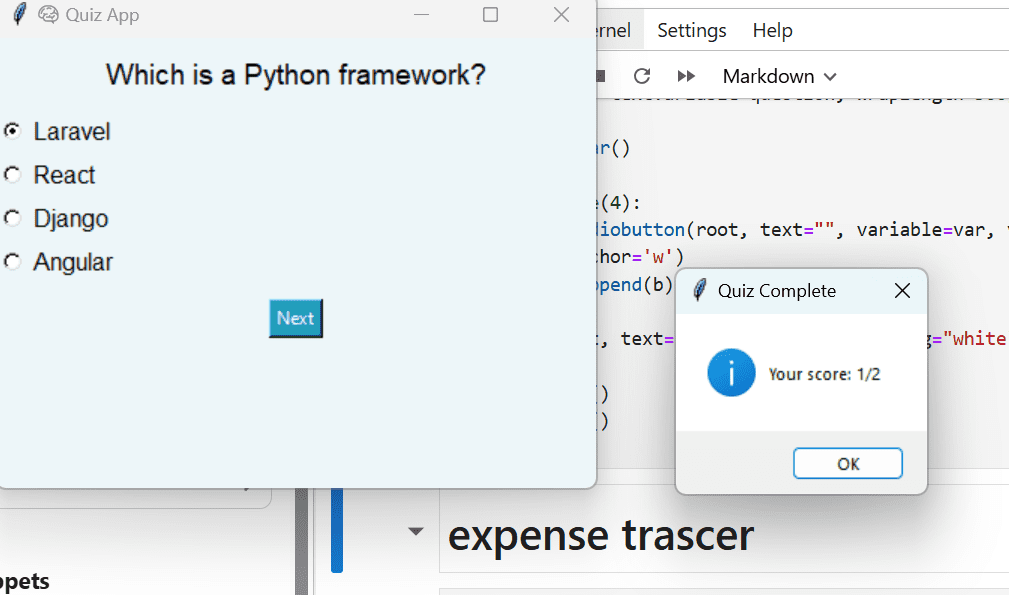
messagebox.showinfo("Quiz Complete", f"Your score: {score}/{len(questions)}")
root.quit()
Gets the selected radio button index.
Compares it with the correct answer and updates the score.
Moves to the next question or shows the final score when the quiz is over.
6. Setting Up the GUI Window
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("🧠 Quiz App")
root.geometry("400x300")
root.config(bg="#edf6f9")
Creates the main application window.
Sets title, size, and background color.
7. Creating the Question Label
question = tk.StringVar()
tk.Label(root, textvariable=question, wraplength=300, font=("Arial", 14), bg="#edf6f9").pack(pady=10)
Displays the current question using a
Labelwith aStringVarto update dynamically.
8. Creating Answer Options as Radio Buttons
var = tk.IntVar()
options = []
for i in range(4):
b = tk.Radiobutton(root, text="", variable=var, value=i, bg="#edf6f9", font=("Arial", 12))
b.pack(anchor='w')
options.append(b)
Uses
IntVarto store the selected option index.Creates 4 radio buttons and appends them to the
optionslist.
9. Next Button
tk.Button(root, text="Next", bg="#219ebc", fg="white", command=check_answer).pack(pady=10)
Clicking the “Next” button triggers the
check_answerfunction.
10. Start the Quiz
load_question()
root.mainloop()
load_question()loads the first question.mainloop()keeps the GUI window open and responsive.
source code
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
questions = [
{"q": "What is the capital of France?", "a": ["Paris", "London", "Rome", "Berlin"], "c": "Paris"},
{"q": "Which is a Python framework?", "a": ["Laravel", "React", "Django", "Angular"], "c": "Django"},
]
current_q = 0
score = 0
def load_question():
q = questions[current_q]
question.set(q['q'])
for i in range(4):
options[i].config(text=q['a'][i])
def check_answer():
global current_q, score
selected = var.get()
if questions[current_q]['a'][selected] == questions[current_q]['c']:
score += 1
current_q += 1
if current_q < len(questions):
load_question()
else:
messagebox.showinfo("Quiz Complete", f"Your score: {score}/{len(questions)}")
root.quit()
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("🧠 Quiz App")
root.geometry("400x300")
root.config(bg="#edf6f9")
question = tk.StringVar()
tk.Label(root, textvariable=question, wraplength=300, font=("Arial", 14), bg="#edf6f9").pack(pady=10)
var = tk.IntVar()
options = []
for i in range(4):
b = tk.Radiobutton(root, text="", variable=var, value=i, bg="#edf6f9", font=("Arial", 12))
b.pack(anchor='w')
options.append(b)
tk.Button(root, text="Next", bg="#219ebc", fg="white", command=check_answer).pack(pady=10)
load_question()
root.mainloop()
output