cryptography app in python using gui
introduction
In the digital age, data security and privacy are more important than ever. From messaging apps to secure websites, encryption forms the backbone of digital communication. This Cryptography Appin python introduces the fundamentals of encryption and decryption through a user-friendly graphical interface built in Python using Tkinter, and implemented interactively in Jupyter Notebook.
The app uses the Caesar Cipher, one of the simplest and oldest encryption techniques. Developed by Julius Caesar for secure communication, it works by shifting each letter in a message by a fixed number of positions in the alphabet. Despite its simplicity, it remains a useful way to demonstrate core encryption principles like substitution, character encoding, and key-based transformation.
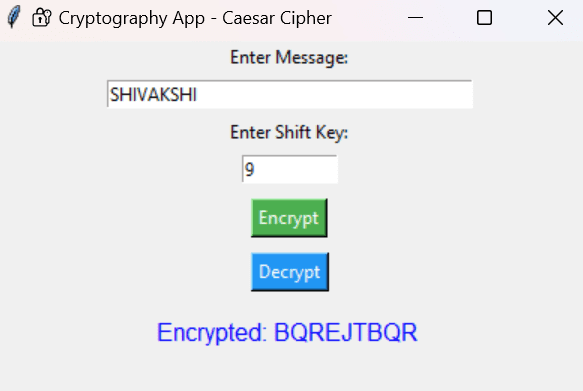
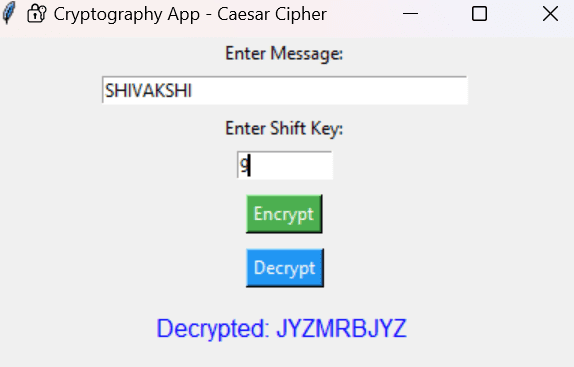
This project lets users type a message, enter a numeric shift key, and then click Encrypt or Decrypt to see how the message transforms. Whether you’re a beginner in cryptography, a Python student, or someone curious about how encryption works, this app gives you an interactive and visual learning experience.
What Makes It Special?
-
Interactive Learning: See how text transforms in real time with just a click.
-
Hands-On GUI: Learn GUI development with Tkinter while understanding cryptographic logic.
-
Error Handling: Includes input validation for a smooth user experience.
-
Modular Design: Built with reusable functions for encryption and decryption.
Use Cases
-
Educational demonstrations in computer science classrooms.
-
Fun Python projects for students learning about strings and algorithms.
-
Simple encryption tool for personal text-based experimentation.
This app is a stepping stone toward building more advanced encryption tools and understanding how real-world cryptographic systems work under the hood. It blends algorithmic logic with user-friendly design, making cryptography both accessible and enjoyable.
steps to create cryptography app
Step 1: Set Up Your Environment
Open Jupyter Notebook.
Make sure Tkinter is available (comes by default with Python).
Optionally, ensure
pip install notebookis run if Jupyter is not already installed.
Step 2: Import Required Libraries
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
tkinter: For building GUI windows.messagebox: To display error or confirmation popups.
Step 3: Define Encryption & Decryption Functions
def encrypt(text, shift):
result = ""
for char in text:
if char.isalpha():
base = ord('A') if char.isupper() else ord('a')
result += chr((ord(char) - base + shift) % 26 + base)
else:
result += char
return result
def decrypt(text, shift):
return encrypt(text, -shift)
Implements Caesar Cipher.
Works for both uppercase and lowercase letters.
Keeps non-alphabet characters (spaces, punctuation) unchanged.
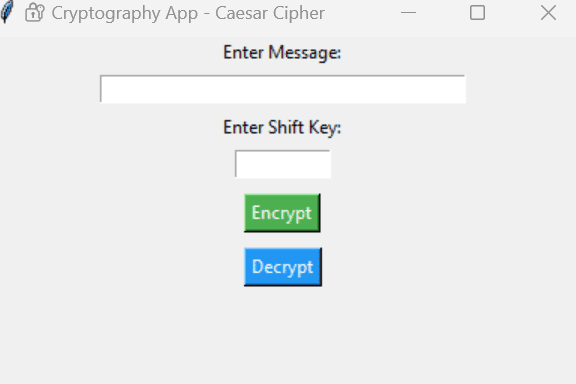
Step 4: Create the GUI App
def launch_app():
def encrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get()
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get())
encrypted = encrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Encrypted: {encrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
def decrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get()
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get())
decrypted = decrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Decrypted: {decrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
app = tk.Tk()
app.title("Cryptography App - Caesar Cipher")
app.geometry("400x300")
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Message:").pack()
message_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=40)
message_entry.pack(pady=5)
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Shift Key:").pack()
key_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=10)
key_entry.pack(pady=5)
tk.Button(app, text="Encrypt", command=encrypt_message, bg="#4CAF50", fg="white").pack(pady=5)
tk.Button(app, text="Decrypt", command=decrypt_message, bg="#2196F3", fg="white").pack(pady=5)
result_var = tk.StringVar()
tk.Label(app, textvariable=result_var, font=("Arial", 12), fg="blue").pack(pady=10)
app.mainloop()
Creates the full GUI with input fields, buttons, and result label.
Adds functions to handle encryption/decryption logic on button click.
Step 5: Launch the App
launch_app()
This line starts the app when run in a cell.
Optional Improvements:
Add a clear/reset button.
Add copy to clipboard feature.
Add support for custom alphabet or multi-language characters.
code explanation
1. Importing Libraries
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
tkinter: For building the graphical user interface (GUI).messagebox: For showing error or info messages (e.g., invalid input).
2. Caesar Cipher Functions
🔸 Encrypt Function
def encrypt(text, shift):
result = ""
for char in text:
if char.isalpha(): # Only encrypt letters
base = ord('A') if char.isupper() else ord('a') # Maintain case
result += chr((ord(char) - base + shift) % 26 + base)
else:
result += char # Keep spaces, punctuation unchanged
return result
🔸 Decrypt Function
def decrypt(text, shift):
return encrypt(text, -shift)
Uses the same
encrypt()function but with the opposite shift to reverse the encryption.
3. GUI App Initialization
def launch_app():
Encapsulates the entire Tkinter app in one function so it can be called easily.
4. Encrypt Button Functionality
def encrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get() # Get message from user input
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get()) # Get shift key and convert to integer
encrypted = encrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Encrypted: {encrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
Takes user input and shift key, runs the encryption, and shows result.
If shift is not an integer, it shows an error popup.
5. Decrypt Button Functionality
def decrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get()
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get())
decrypted = decrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Decrypted: {decrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
Same as encrypt but uses the decryption function.
6. GUI Layout
app = tk.Tk()
app.title(" Cryptography App - Caesar Cipher")
app.geometry("400x300")
Creates the main window with title and size.
🔹 Message Input
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Message:").pack()
message_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=40)
message_entry.pack(pady=5)
🔹 Shift Key Input
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Shift Key:").pack()
key_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=10)
key_entry.pack(pady=5)
🔹 Buttons for Action
tk.Button(app, text="Encrypt", command=encrypt_message).pack(pady=5)
tk.Button(app, text="Decrypt", command=decrypt_message).pack(pady=5)
🔹 Output Display
result_var = tk.StringVar()
tk.Label(app, textvariable=result_var, font=("Arial", 12), fg="blue").pack(pady=10)
7. Run the App
app.mainloop()
Starts the GUI loop, waits for user interaction.
Final Call to Launch
launch_app()
Calls the function to launch the GUI.
What It Does
Accepts text and a numeric shift key from the user.
Encrypts or decrypts using the Caesar Cipher.
Shows the result in the GUI.
Handles invalid input with error messages.
source code
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
def encrypt(text, shift):
result = ""
for char in text:
if char.isalpha():
base = ord('A') if char.isupper() else ord('a')
result += chr((ord(char) - base + shift) % 26 + base)
else:
result += char
return result
def decrypt(text, shift):
return encrypt(text, -shift)
def launch_app():
def encrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get()
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get())
encrypted = encrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Encrypted: {encrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
def decrypt_message():
msg = message_entry.get()
try:
shift = int(key_entry.get())
decrypted = decrypt(msg, shift)
result_var.set(f"Decrypted: {decrypted}")
except:
messagebox.showerror("Invalid", "Shift must be an integer.")
app = tk.Tk()
app.title(" Cryptography App - Caesar Cipher")
app.geometry("400x300")
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Message:").pack()
message_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=40)
message_entry.pack(pady=5)
tk.Label(app, text="Enter Shift Key:").pack()
key_entry = tk.Entry(app, width=10)
key_entry.pack(pady=5)
tk.Button(app, text="Encrypt", command=encrypt_message, bg="#4CAF50", fg="white").pack(pady=5)
tk.Button(app, text="Decrypt", command=decrypt_message, bg="#2196F3", fg="white").pack(pady=5)
result_var = tk.StringVar()
tk.Label(app, textvariable=result_var, font=("Arial", 12), fg="blue").pack(pady=10)
app.mainloop()
launch_app()
output