interview question app in python using GUI
introduction
In today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape, landing a job often requires more than just academic knowledge—it demands practical expertise, confidence, and continuous self-evaluation. Whether you’re preparing for your first job interview or planning a switch to a better opportunity, practicing real-world interview questions is crucial. To assist candidates in this journey, the Interview Preparation App offers a smart and interactive way to learn, revise, and test interview questions app in python right from your desktop.
This application, built entirely in Python using Tkinter, is a lightweight, standalone GUI program designed to simulate the experience of reviewing and answering interview questions. It combines the advantages of a study tool and quiz app in a simple, elegant interface.
Purpose of the Application
The Interview Preparation App serves as a personalized digital tutor that:
Enables users to explore topic-wise questions and answers.
Facilitates self-assessment through quizzes.
Provides instant feedback to reinforce learning.
Instead of passively reading notes or web articles, users can actively participate in mock quizzes, making the learning process more engaging, interactive, and memorable.
Technology Used
Python: Core programming language.
Tkinter: Built-in GUI library in Python for building the user interface.
ttk module: For advanced and styled widgets like
Combobox.messagebox & simpledialog: For interactive user dialogs and alerts.
Core Functionalities
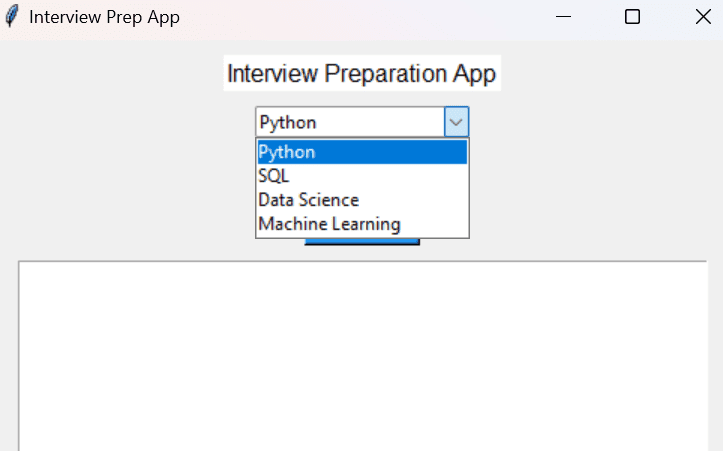
Topic Dropdown Menu
Users can select a topic (e.g., Python, SQL, Machine Learning, etc.) from a dropdown menu powered by thettk.Combobox.Show Questions
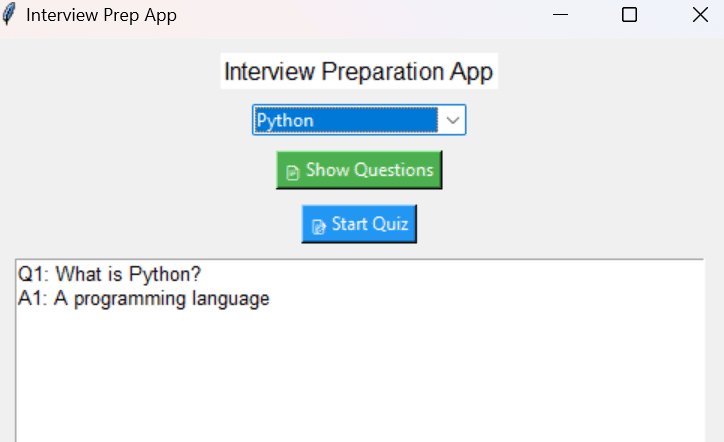
Clicking the “📄 Show Questions” button fetches and displays all questions and answers related to the selected topic in a scrollableTextarea. This helps users revise and read content quickly.Start Quiz
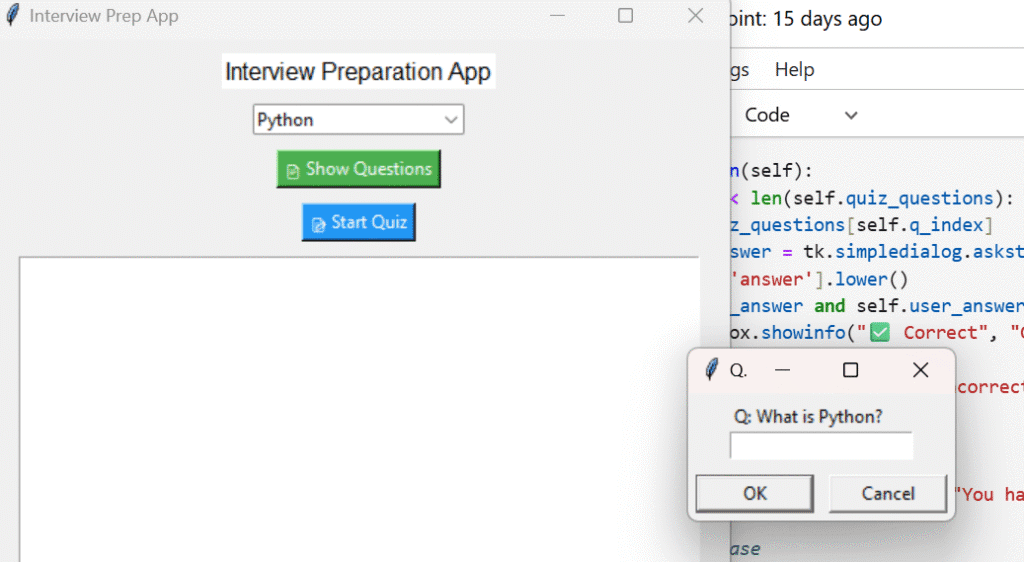
Clicking the ” Start Quiz” button initiates a quiz for the selected topic. Each question appears one by one using a popup input box (simpledialog.askstring), allowing users to answer in real-time. After submission:If the answer is correct: A success message is shown.
If incorrect: The correct answer is displayed.
The quiz continues until all topic questions are covered.
Feedback System
Correctness is validated using case-insensitive matching, and feedback is shown using messageboxes, giving the user immediate insight into their performance.
Modular Design and Extensibility
The app is easily extendable. New topics and questions can be added to the
questions_dblist.In future versions, features like score tracking, timers, progress reports, or even database integration (SQLite/MySQL) can be included.
Supports offline usage, making it a great companion for last-minute revision.
Ideal For
Students appearing for campus placements.
Software developers and data scientists preparing for interviews.
Anyone preparing for roles involving coding, analytics, or technical discussions.
Learning Outcomes
By using this app, users will:
Reinforce key concepts in Python, SQL, and data science.
Build confidence through active recall and repetition.
Learn to think under pressure and improve time-based response skills.
steps to create interview question app in python
Step 1: Set Up Your Environment
Install Python (if not already installed)
Download from https://www.python.orgChoose an IDE or code editor
Examples: VS Code, PyCharm, or just use IDLE (comes with Python).
Step 2: Import Required Libraries
Start your Python file by importing all necessary modules:
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox, simpledialog
These are built-in libraries in Python for GUI development. No extra installation is needed.
Step 3: Create the Main Class and Constructor
Define a class InterviewApp that will manage the GUI components and application logic:
class InterviewApp:
def __init__(self, root):
...
Inside this constructor:
Set the window title and size
Create a dropdown for topics
Create buttons for “Show Questions” and “Start Quiz”
Add a text area for displaying questions and answers
Step 4: Create the Topic Dropdown
Use ttk.Combobox for a clean dropdown to select topics:
self.selected_topic = tk.StringVar()
self.topics = ["Python", "SQL", "Data Science", "Machine Learning"]
ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable=self.selected_topic, values=self.topics, state="readonly").pack()
Step 5: Add Buttons and Text Area
Add two buttons:
Show Questions – to view questions and answers
Start Quiz – to start the quiz
tk.Button(root, text=" Show Questions", command=self.show_questions).pack()
tk.Button(root, text=" Start Quiz", command=self.start_quiz).pack()
self.output = tk.Text(root)
self.output.pack()
Step 6: Define the show_questions() Function
This function filters the question bank based on the selected topic and shows the questions and answers in the text area.
def show_questions(self):
topic = self.selected_topic.get()
...
Use:
self.output.insert(tk.END, f"Q: {q['question']}\nA: {q['answer']}\n\n")
Step 7: Define the start_quiz() Function
This function starts the quiz for the selected topic:
def start_quiz(self):
topic = self.selected_topic.get()
self.quiz_questions = [q for q in questions_db if q["topic"] == topic]
self.q_index = 0
self.ask_next_question()
Step 8: Define the ask_next_question() Function
This will:
Show questions one-by-one using a popup
Compare user input with correct answer
Give feedback using
messagebox
def ask_next_question(self):
if self.q_index < len(self.quiz_questions):
q = self.quiz_questions[self.q_index]
self.user_answer = tk.simpledialog.askstring("Quiz", f"Q: {q['question']}")
if self.user_answer.lower() in q['answer'].lower():
messagebox.showinfo(" Correct", "Good job!")
else:
messagebox.showwarning(" Incorrect", f"Correct Answer: {q['answer']}")
self.q_index += 1
self.ask_next_question()
else:
messagebox.showinfo("Quiz Done", "You have completed the quiz!")
Step 9: Define the Questions Database
This is a list of dictionaries where each dictionary contains:
topicquestionanswer
questions_db = [
{"topic": "Python", "question": "What is Python?", "answer": "A programming language"},
{"topic": "SQL", "question": "What does SQL stand for?", "answer": "Structured Query Language"},
...
]
Step 10: Launch the App
At the bottom of the file, add:
root = tk.Tk()
app = InterviewApp(root)
root.mainloop()
This initializes the main window and starts the Tkinter event loop.
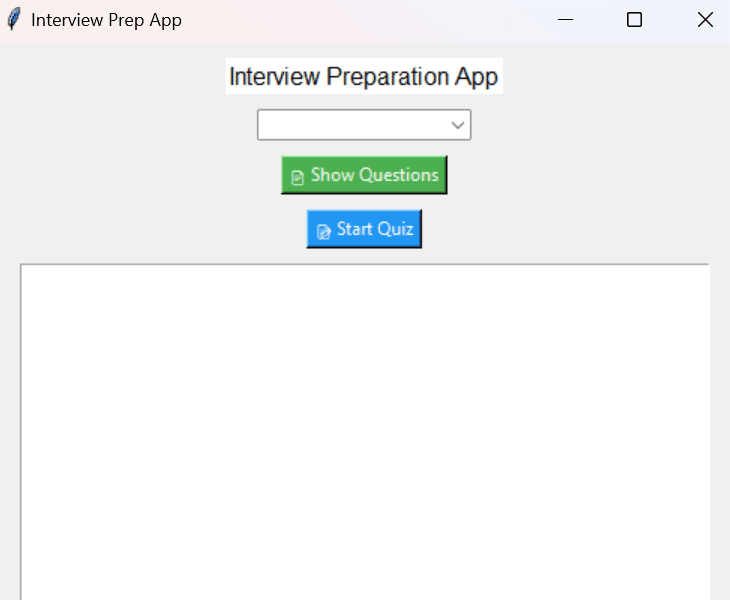
Output:
A window with topic dropdown, two buttons, and a text box.
Clicking “Show Questions” displays Q&A for selected topic.
Clicking “Start Quiz” starts a quiz with instant feedback.
code explanation
1. Import Required Modules
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox, simpledialog
tkinter: Core GUI module.ttk: For themed widgets likeCombobox.messagebox: To show popup messages.simpledialog: To take text input from the user during the quiz.
2. Class: InterviewApp
class InterviewApp:
Defines the main GUI logic of the app.
3. Constructor: __init__
def __init__(self, root):
Initializes the UI components.
Dropdown Menu (Combobox) for topic selection.
Buttons:
Show Questions – Displays Q&A from the database.
Start Quiz – Starts a quiz for the selected topic.
Text Widget to display questions and answers.
Key Variables:
self.selected_topic: Stores the user’s selected topic.self.quiz_questions: Stores questions for the quiz.self.q_index: Tracks current quiz question index.
4. show_questions()
def show_questions(self):
Triggered by Show Questions button.
Filters questions from
questions_dbbased on selected topic.Clears the
Textarea and inserts matching Q&A.
filtered = [q for q in questions_db if q["topic"] == topic]
5. start_quiz()
def start_quiz(self):
Triggered by Start Quiz button.
Filters topic-based questions.
If available, starts the quiz via
ask_next_question().If none, shows info box.
6. ask_next_question()
def ask_next_question(self):
Presents a question using a popup input box.
Compares user’s input (case-insensitive) with the correct answer.
Shows success or failure message.
Proceeds to next question or ends the quiz.
Logic:
self.user_answer.lower() in correct
This allows partial matching (e.g., “language” matches “a programming language”).
7. Questions Database: questions_db
questions_db = [
{"topic": "Python", "question": "What is Python?", "answer": "A programming language"},
...
]
You can expand this list with more Q&A under various topics like SQL, Machine Learning, etc.
8. App Launch
root = tk.Tk()
app = InterviewApp(root)
root.mainloop()
Initializes the main window.
Starts the event loop.
Suggestions for Enhancement
Add more questions for each topic.
Store questions in an external file or database.
Track scores and provide a final result.
Add images or explanations for better learning.
source code
#### import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import ttk, messagebox
# Sample Questions Database
questions_db = [
{
"topic": "Python",
"question": "What is the difference between a list and a tuple?",
"answer": "Lists are mutable, tuples are immutable."
},
{
"topic": "OOP",
"question": "What is inheritance in OOP?",
"answer": "Inheritance allows a class to acquire properties and methods of another class."
},
{
"topic": "DSA",
"question": "What is a stack and how does it work?",
"answer": "A stack is a linear data structure that works on LIFO principle (Last In First Out)."
},
{
"topic": "Python",
"question": "What are Python decorators?",
"answer": "Decorators are functions that modify the functionality of another function without changing its code."
},
{
"topic": "OOP",
"question": "What is polymorphism?",
"answer": "Polymorphism allows functions or methods to process objects differently based on their data type or class."
}
]
# Main Application Class
class InterviewApp:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title(" Interview Q&A App")
self.root.geometry("600x400")
self.root.config(bg="white")
# Dropdown for topics
self.topics = sorted(set(q["topic"] for q in questions_db))
self.selected_topic = tk.StringVar(value=self.topics[0])
tk.Label(root, text="Select Topic:", font=("Arial", 12), bg="white").pack(pady=10)
ttk.Combobox(root, textvariable=self.selected_topic, values=self.topics, state="readonly").pack()
# Buttons
tk.Button(root, text=" Show Questions", command=self.show_questions, bg="#4CAF50", fg="white").pack(pady=10)
tk.Button(root, text=" Start Quiz", command=self.start_quiz, bg="#2196F3", fg="white").pack()
# Text area
self.output = tk.Text(root, height=12, wrap="word", font=("Arial", 10))
self.output.pack(padx=20, pady=10, fill="both", expand=True)
def show_questions(self):
topic = self.selected_topic.get()
filtered = [q for q in questions_db if q["topic"] == topic]
self.output.delete("1.0", tk.END)
for i, q in enumerate(filtered, 1):
self.output.insert(tk.END, f"Q{i}: {q['question']}\n")
self.output.insert(tk.END, f"A{i}: {q['answer']}\n\n")
def start_quiz(self):
topic = self.selected_topic.get()
self.quiz_questions = [q for q in questions_db if q["topic"] == topic]
self.q_index = 0
if not self.quiz_questions:
messagebox.showinfo("No Questions", "No questions available for this topic.")
return
self.ask_next_question()
def ask_next_question(self):
if self.q_index < len(self.quiz_questions):
q = self.quiz_questions[self.q_index]
self.user_answer = tk.simpledialog.askstring("Quiz", f"Q: {q['question']}")
correct = q['answer'].lower()
if self.user_answer and self.user_answer.lower() in correct:
messagebox.showinfo(" Correct", "Good job!")
else:
messagebox.showwarning(" Incorrect", f"Correct Answer: {q['answer']}")
self.q_index += 1
self.ask_next_question()
else:
messagebox.showinfo("Quiz Done", "You have completed the quiz!")
# Launch the App
root = tk.Tk()
app = InterviewApp(root)
root.mainloop()
output