ludo game in python using gui and thinkter

introduction
The “ludo game in python“ project is a simplified digital version of the traditional Ludo board game, implemented in Python using the Tkinter GUI toolkit. Ludo is a strategy-based multiplayer board game played with a dice and tokens, where the aim is to move your token around the board and reach the final cell before your opponents.
In this project, we recreate a basic simulation of the Ludo experience by focusing on the core gameplay elements:
-
Rolling a dice
-
Moving a token forward
-
Switching turns among players
-
Determining a winner
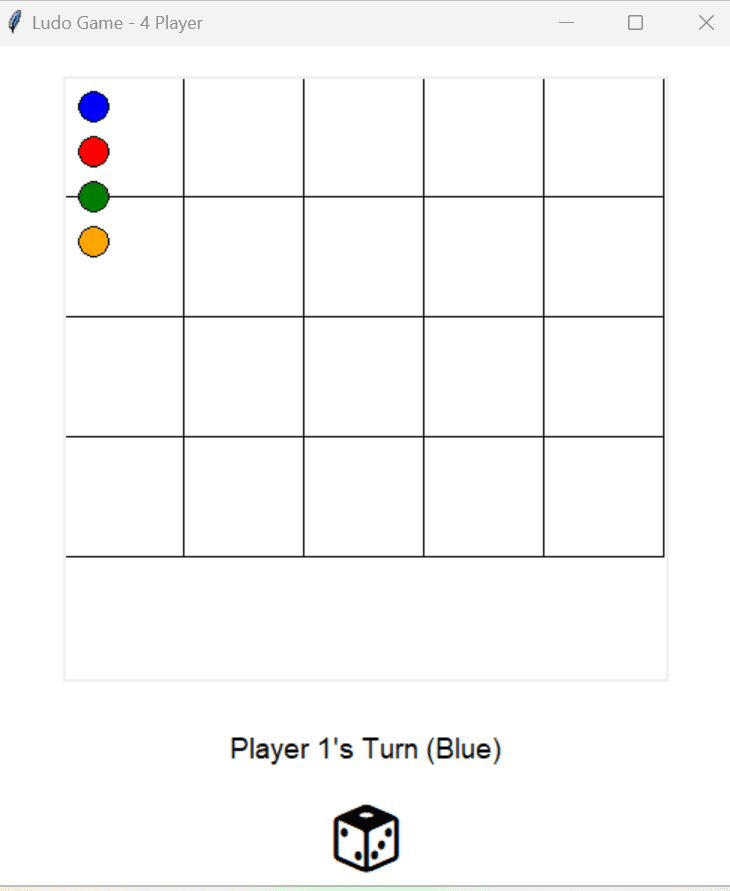
This version of the game supports four players, each represented by a distinct color (blue, red, green, orange). Every player takes turns to roll a virtual dice, and based on the result (a number between 1 and 6), their token advances that many steps on a 20-cell board. The player who reaches the last cell first is declared the winner.
The graphical interface has been built using Tkinter’s canvas, which allows us to visually represent the board and moving tokens. The board is displayed as a 4×5 grid of square cells, and tokens are drawn as colored circles (ovals) on the canvas. The dice is represented by a large number on screen, and players interact with the game by clicking the “Roll Dice” button.
Key Features:
-
Dice Roll Simulation using
random.randint() -
Canvas-based Board and Token Movement
-
Turn-based System for 4 Players
-
Win Condition Detection
-
Interactive GUI Components (buttons, labels, visual updates)
This project is designed to demonstrate:
-
Basic object-oriented programming using Python classes
-
GUI development with Tkinter
-
Handling canvas graphics and event-driven logic
-
Creating a fun and visual representation of a classic board game
Purpose of the Project:
-
To explore the fundamentals of GUI programming in Python
-
To simulate a real-world gameplay of ludo game in python experience
-
To practice event handling, loop control, and canvas drawing
-
To build a visually interactive application with player feedback
steps to create ludo game
Step 1: Import Required Modules
Start by importing the necessary libraries.
import tkinter as tk
import random
tkinteris used for building the GUI.randomis used to simulate dice rolls (random numbers from 1 to 6).
Step 2: Create the Main Function
Define a function to run the game so everything is encapsulated.
def run_ludo_game():
Step 3: Define the LudoGame Class
Create a class to encapsulate the full logic and GUI.
class LudoGame:
def __init__(self, root):
...
The constructor (
__init__) initializes game state, GUI elements, and tokens.
Step 4: Set Up the Window
Inside the __init__ method:
self.root = root
self.root.title("Ludo Game - 4 Player")
self.root.geometry("500x600")
self.root.config(bg="white")
Sets the title, size, and background of the main window.
Step 5: Initialize Game Variables
self.turn = 0
self.positions = [0, 0, 0, 0]
self.colors = ["blue", "red", "green", "orange"]
turn: tracks which player’s turn it is (0 to 3).positions: list of positions of each player’s token on the board.colors: token color for each player.
Step 6: Create the Game Board
Create a canvas to draw the board grid and tokens:
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(root, width=400, height=400, bg="white")
self.canvas.pack(pady=20)
Draw 20 cells (4 rows × 5 columns) on the canvas:
self.cells = []
def make_board(self):
for i in range(20):
x = (i % 5) * 80
y = (i // 5) * 80
self.canvas.create_rectangle(x, y, x+80, y+80, outline="black")
self.cells.append((x + 20, y + 20))
Step 7: Create Player Tokens
self.tokens = [
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 10, 30, 30, fill="blue"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 40, 30, 60, fill="red"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 70, 30, 90, fill="green"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 100, 30, 120, fill="orange")
]
Each token is a small colored circle initially placed outside the board.
Step 8: Add Labels and Dice Display
self.label = tk.Label(root, text="Player 1's Turn (Blue)", font=("Arial", 14), bg="white")
self.label.pack(pady=10)
self.dice_label = tk.Label(root, text="🎲", font=("Arial", 40), bg="white")
self.dice_label.pack()
A label shows which player’s turn it is.
The dice result is displayed as a large number.
Step 9: Create the Roll Dice Button
self.roll_btn = tk.Button(root, text="Roll Dice", font=("Arial", 14), bg="#4CAF50", fg="white", command=self.roll_dice)
self.roll_btn.pack(pady=10)
Clicking the button triggers a dice roll and moves the token.
Step 10: Define the Dice Roll Logic
def roll_dice(self):
roll = random.randint(1, 6)
self.dice_label.config(text=str(roll))
self.move_token(self.turn, roll)
self.turn = (self.turn + 1) % 4
color = self.colors[self.turn].capitalize()
self.label.config(text=f"Player {self.turn+1}'s Turn ({color})")
Generates a random number between 1 and 6.
Moves the current player’s token.
Advances to the next player.
Step 11: Define Token Movement Logic
def move_token(self, player, steps):
self.positions[player] += steps
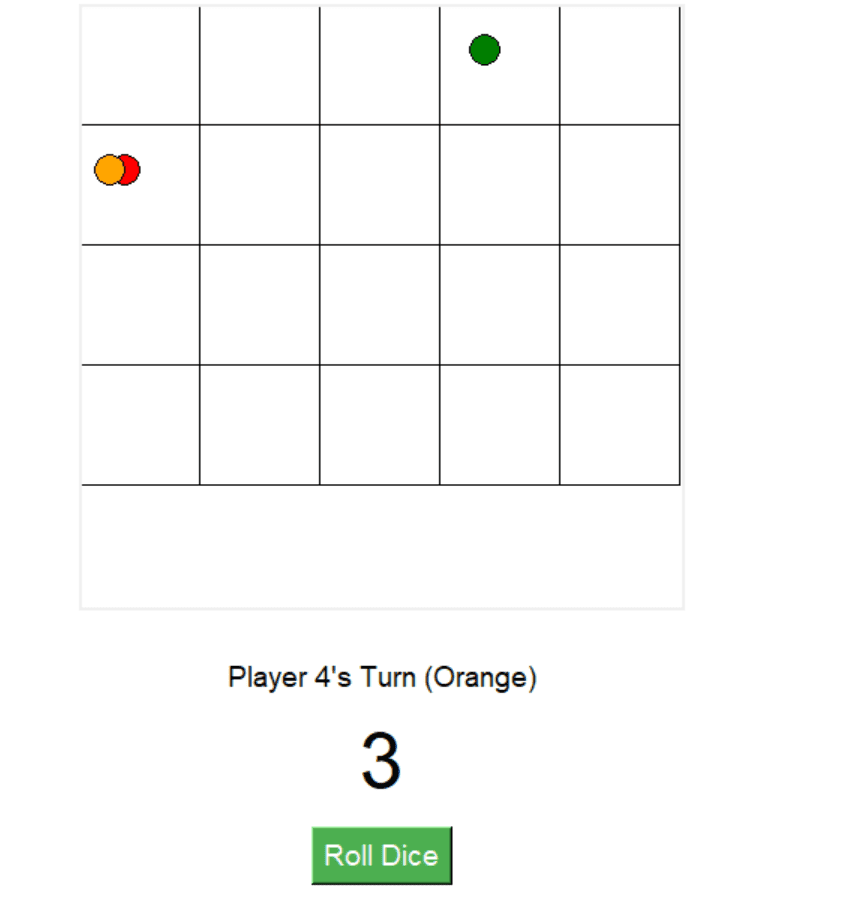
if self.positions[player] >= len(self.cells):
self.label.config(text=f"🎉 Player {player+1} Wins!")
self.roll_btn.config(state="disabled")
return
x, y = self.cells[self.positions[player]]
self.canvas.coords(self.tokens[player], x, y, x+20, y+20)
Updates player’s position based on the dice roll.
Checks if the player reached the end and declares winner.
Step 12: Run the Game
Finally, call the game:
root = tk.Tk()
game = LudoGame(root)
root.mainloop()
And then outside the function:
run_ludo_game()
code explanation
1.Import Thinkter
import tkinter as tk
import random
tkinteris imported to build the GUI.randomis used to simulate dice rolls (random numbers from 1 to 6).
def run_ludo_game():
Defines a function to encapsulate the game setup and execution.
class LudoGame:
def __init__(self, root):
Defines the
LudoGameclass.__init__method sets up the initial game state and GUI elements.rootis the main window passed as a parameter.
2.Window Setup
self.root = root
self.root.title("Ludo Game - 4 Player")
self.root.geometry("500x600")
self.root.config(bg="white")
Sets the window title, size, and background color.
3.Game Variables
self.turn = 0
self.positions = [0, 0, 0, 0]
self.colors = ["blue", "red", "green", "orange"]
turn: keeps track of which player’s turn (0 to 3).positions: stores the cell number each player is currently on.colors: color assigned to each player’s token.
4.Canvas Board
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(root, width=400, height=400, bg="white")
self.canvas.pack(pady=20)
A drawing space (canvas) where the game board and tokens appear.
self.cells = []
self.make_board()
Initializes the list of cell coordinates.
Calls
make_board()to draw 20 rectangles as the game path.
5.Player Tokens
self.tokens = [
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 10, 30, 30, fill="blue"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 40, 30, 60, fill="red"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 70, 30, 90, fill="green"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 100, 30, 120, fill="orange")
]
Draws 4 oval-shaped tokens with different colors, initially off the board.
6.Status Label and Dice
self.label = tk.Label(root, text="Player 1's Turn (Blue)", font=("Arial", 14), bg="white")
self.label.pack(pady=10)
self.dice_label = tk.Label(root, text="🎲", font=("Arial", 40), bg="white")
self.dice_label.pack()
label: shows whose turn it is.dice_label: large label showing the dice number after rolling.
7.Roll Button
self.roll_btn = tk.Button(root, text="Roll Dice", font=("Arial", 14), bg="#4CAF50", fg="white", command=self.roll_dice)
self.roll_btn.pack(pady=10)
Button triggers a dice roll.
Calls the method
roll_dice()when clicked.
8.Create the Board
def make_board(self):
for i in range(20):
x = (i % 5) * 80
y = (i // 5) * 80
self.canvas.create_rectangle(x, y, x+80, y+80, outline="black")
self.cells.append((x + 20, y + 20))
Draws a 5×4 board (20 cells).
Calculates the top-left corner of each square.
Saves the center positions (x+20, y+20) in
self.cellsfor token placement.
9.Move Tokens
def move_token(self, player, steps):
self.positions[player] += steps
if self.positions[player] >= len(self.cells):
self.label.config(text=f"🎉 Player {player+1} Wins!")
self.roll_btn.config(state="disabled")
return
x, y = self.cells[self.positions[player]]
self.canvas.coords(self.tokens[player], x, y, x+20, y+20)
Moves the token of the current player forward by
steps.If token reaches or passes the last cell, declares that player as the winner.
Updates the position of the token on the canvas using
.coords().
10.Dice Roll Logic
def roll_dice(self):
roll = random.randint(1, 6)
self.dice_label.config(text=str(roll))
self.move_token(self.turn, roll)
self.turn = (self.turn + 1) % 4
color = self.colors[self.turn].capitalize()
self.label.config(text=f"Player {self.turn+1}'s Turn ({color})")
Simulates a dice roll (1–6).
Calls
move_token()for the current player.Advances to the next player using modulo logic.
Updates the label to show whose turn is next.
11.Start the Game
root = tk.Tk()
game = LudoGame(root)
root.mainloop()
Creates the main application window.
Starts an instance of
LudoGame.Runs the GUI event loop using
mainloop().
12.Final Line: Run the Function
run_ludo_game()
Starts the game when the script is executed.
13.Summary of Logic
| Component | Role |
|---|---|
Canvas | Draws the board and tokens |
Label | Shows player turns and results |
Button | Rolls the dice and triggers token movement |
tokens[] | Stores reference to each player’s token (oval) |
positions[] | Tracks how many steps each player has moved |
make_board() | Draws the 20-cell game path |
move_token() | Updates a player’s token position |
roll_dice() | Rolls the dice and controls player turns |
source code
import tkinter as tk
import random
def run_ludo_game():
class LudoGame:
def __init__(self, root):
self.root = root
self.root.title("Ludo Game - 4 Player")
self.root.geometry("500x600")
self.root.config(bg="white")
self.turn = 0
self.positions = [0, 0, 0, 0]
self.colors = ["blue", "red", "green", "orange"]
self.canvas = tk.Canvas(root, width=400, height=400, bg="white")
self.canvas.pack(pady=20)
self.cells = []
self.make_board()
self.tokens = [
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 10, 30, 30, fill="blue"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 40, 30, 60, fill="red"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 70, 30, 90, fill="green"),
self.canvas.create_oval(10, 100, 30, 120, fill="orange")
]
self.label = tk.Label(root, text="Player 1's Turn (Blue)", font=("Arial", 14), bg="white")
self.label.pack(pady=10)
self.dice_label = tk.Label(root, text="🎲", font=("Arial", 40), bg="white")
self.dice_label.pack()
self.roll_btn = tk.Button(root, text="Roll Dice", font=("Arial", 14), bg="#4CAF50", fg="white", command=self.roll_dice)
self.roll_btn.pack(pady=10)
def make_board(self):
for i in range(20):
x = (i % 5) * 80
y = (i // 5) * 80
self.canvas.create_rectangle(x, y, x+80, y+80, outline="black")
self.cells.append((x + 20, y + 20))
def move_token(self, player, steps):
self.positions[player] += steps
if self.positions[player] >= len(self.cells):
self.label.config(text=f"🎉 Player {player+1} Wins!")
self.roll_btn.config(state="disabled")
return
x, y = self.cells[self.positions[player]]
self.canvas.coords(self.tokens[player], x, y, x+20, y+20)
def roll_dice(self):
roll = random.randint(1, 6)
self.dice_label.config(text=str(roll))
self.move_token(self.turn, roll)
self.turn = (self.turn + 1) % 4
color = self.colors[self.turn].capitalize()
self.label.config(text=f"Player {self.turn+1}'s Turn ({color})")
root = tk.Tk()
game = LudoGame(root)
root.mainloop()
run_ludo_game()
output