Currency Converter in Java Using Swing With Source Code
Introduction:
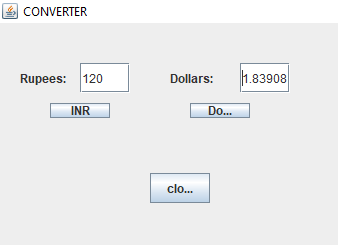
The Java program that creates a simple currency converter using the Swing library. The program creates a GUI that consists of two labels(one for rupees and one for dollars), two text fields (one for rupee input and one for dollar input), and three buttons (One to convert rupees to dollars, one to convert dollars to rupees, and one to close the program).
Explanation:
Java is a popular programming language that is widely used for developing various types of applications, including desktop applications. One of the key features of Java is its ability to create graphical user interfaces (GUIs) using the Java Swing library. In this article, we will take a closer look at a Java program that demonstrates how to create a currency converter GUI using the Java Swing library.
The program begins by importing the necessary classes from the Java Swing library, including the JFrame, JLabel, JTextField, JButton, and ActionListener classes. The program then defines a function called “converter” that creates the GUI for the currency converter.
The first step in creating the GUI is to create a new frame using the JFrame class and setting its title to “CONVERTER”. The program then creates two labels, one for rupees and one for dollars, and sets their bounds on the frame. The program also creates two text fields, one for rupees and one for dollars, and sets their bounds on the frame. The text fields are initialized with the value of 0 by default.
The program then creates three buttons, one for converting rupees to dollars, one for converting dollars to rupees, and one for closing the frame. The buttons are given appropriate labels and are positioned on the frame. The program then adds action listeners to the buttons to listen for user input and perform the conversion calculations.
The program uses the ActionListener class to listen for user input and perform the conversion calculations. When the user clicks the button to convert rupees to dollars, the program retrieves the value from the rupee text field, converts it to a double, and performs the calculation to convert the rupee value to dollars. The program then sets the value of the dollar text field to the result of the calculation. Similarly, when the user clicks the button to convert dollars to rupees, the program retrieves the value from the dollar text field, converts it to a double, and performs the calculation to convert the dollar value to rupees. The program then sets the value of the rupee text field to the result of the calculation.
Source Code:
Get Discount on Top Educational Courses
// Java program to convert from
// rupee to the dollar and vice-versa
// using Java Swing
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class CodeWithCurious {
// Function to convert from rupee
// to the dollar and vice-versa
// using Java Swing
public static void converter() {
// Creating a new frame using JFrame
JFrame f = new JFrame("CONVERTER");
// Creating two labels
JLabel l1, l2;
// Creating two text fields.
// One for rupee and one for
// the dollar
JTextField t1, t2;
// Creating three buttons
JButton b1, b2, b3;
// Naming the labels and setting
// the bounds for the labels
l1 = new JLabel("Rupees:");
l1.setBounds(20, 40, 60, 30);
l2 = new JLabel("Dollars:");
l2.setBounds(170, 40, 60, 30);
// Initializing the text fields with
// 0 by default and setting the
// bounds for the text fields
t1 = new JTextField("0");
t1.setBounds(80, 40, 50, 30);
t2 = new JTextField("0");
t2.setBounds(240, 40, 50, 30);
// Creating a button for INR,
// one button for the dollar
// and one button to close
// and setting the bounds
b1 = new JButton("INR");
b1.setBounds(50, 80, 60, 15);
b2 = new JButton("Dollar");
b2.setBounds(190, 80, 60, 15);
b3 = new JButton("close");
b3.setBounds(150, 150, 60, 30);
// Adding action listener
b1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// Converting to double
double d = Double.parseDouble(t1.getText());
// Converting rupees to dollars
double d1 = (d / 65.25);
// Getting the string value of the
// calculated value
String str1 = String.valueOf(d1);
// Placing it in the text box
t2.setText(str1);
}
});
// Adding action listener
b2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// Converting to double
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(t2.getText());
// converting Dollars to rupees
double d3 = (d2 * 65.25);
// Getting the string value of the
// calculated value
String str2 = String.valueOf(d3);
// Placing it in the text box
t1.setText(str2);
}
});
// Action listener to close the form
b3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
f.dispose();
}
});
// Default method for closing the frame
f.addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter() {
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
}
});
// Adding the created objects
// to the form
f.add(l1);
f.add(t1);
f.add(l2);
f.add(t2);
f.add(b1);
f.add(b2);
f.add(b3);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setSize(400, 300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String args[]) {
converter();
}
}
The program also includes a button to close the frame and a window listener to exit the program when the frame is closed. The program uses the setLayout, setSize, and setVisible methods to set the layout, size, and visibility of the frame, respectively.
In conclusion, this program demonstrates how to create a currency converter GUI using the Java Swing library. It shows how to create a frame, labels, text fields, and buttons, and how to use action listeners to listen for user input and perform the conversion calculations. The program also includes a button to close the frame and a window listener to exit the program when the frame is closed. This program is a good starting point for learning how to create a simple GUI using the Java Swing library.
Output:
Find More Projects
URL Shortener Using Python Django Introduction: Long URLs can be shortened into short, shareable links with the help of the URL Shortener …
User Authentication System Using Python Django Introduction: The implementation of safe and adaptable user authentication in Django is the main goal of …
The E-Learning System using Java with a Graphical User Interface (GUI) Introduction The E-Learning System is developed using Java (with a Graphical …
Weather App Using Python Django Introduction: When a user enters the name of a city, the Weather App retrieves current weather information. …
Quiz App Using Python Django Introduction: Users can take quizzes in a variety of subjects, see their results, and monitor their progress …
resume screener in python using python introduction The hiring process often begins with reviewing numerous resumes to filter out the most suitable …